Cloud Power: How to scale Azure Websites globally with Traffic Manager
The "cloud" is one of those things that I totally get and totally intellectualize, but it still consistently blows me away. And I work on a cloud, too, which is a little ironic that I should be impressed.
I guess part of it is historical context. Today's engineers get mad if a deployment takes 10 minutes or if a scale-out operation has them waiting five. I used to have multi-hour builds and a scale out operation involved a drive over to PC Micro Center. Worse yet, having a Cisco engineer fly in to configure a load balancer. Certainly engineers in the generation before mine could lose hours with a single punch card mistake.
It's the power that impresses me.
And I don't mean CPU power, I mean the power to build, to create, to achieve, in minutes, globally. My that's a lot of comma faults.
Someone told me once that the average middle class person is more powerful than a 15th century king. You eat on a regular basis, can fly across the country in a few hours, you have antibiotics and probably won't die from a scratch.
Cloud power is that. Here's what I did last weekend that blew me away.
I just took a website, bought a wildcard SSL cert, deployed to Asia, Europe, and US, and geo-load-balanced the secure traffic in 45 min. O_O
— Scott Hanselman (@shanselman) May 3, 2014 Here's how I did it.
Scaling an Azure Website globally in minutes, plus adding SSL
I'm working on a little startup with my friend Greg, and I recently deploy our backend service to a small Azure website in "North Central US." I bought a domain name for $8 and setup a CNAME to point to this new Azure website. Setting up custom DNS takes just minutes of course.
Adding SSL to Azure Websites
I want to run my service traffic over SSL, so I headed over to DNSimple where I host my DNS and bought a wildcard SSL for *.mydomain.com for only $100!

Adding the SSL certificate to Azure is easy, you upload it from the Configure tab on Azure Websites, then binding it to your site.

Most SSL certificates are issued as a *.crt file, but Azure and IIS prefer *.pfx. I just downloaded OpenSSL for Windows and ran:
openssl pkcs12 -export -out mysslcert.pfx -inkey myprivate.key -in myoriginalcert.crt
Then I upload mysslcert.pfx to Azure. If you have intermediaries then you might need to include those as well.
This gets me a secure connection to my single webserver, but I need multiple ones as my beta testers in Asia and Europe have complained that my service is slow for them.
Adding multiple global Azure Website locations
It's easy to add more websites, so I made two more, spreading them out a bit.

I use Git deployment for my websites, so I added two extra named remotes in Git. That way I can deploy like this:
>git push azure-NorthCentral master
>git push azure-SoutheastAsia master
>git push azure-WestEurope master
At this point, I've got three web sites in three locations but they aren't associated together in any way.
I also added a "Location" configuration name/value pair for each website so I could put the location at the bottom of the site to confirm when global load balancing is working just by pulling it out like this:
location = ConfigurationManager.AppSettings["Location"];
I could also potentially glean my location by exploring the Environment variables like WEBSITE_SITE_NAME for my application name, which I made match my site's location.
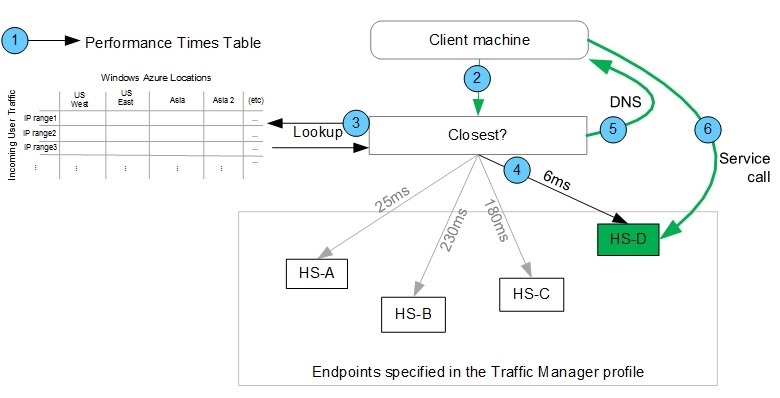
Now I bring these all together by setting up a Traffic Manager in Azure.
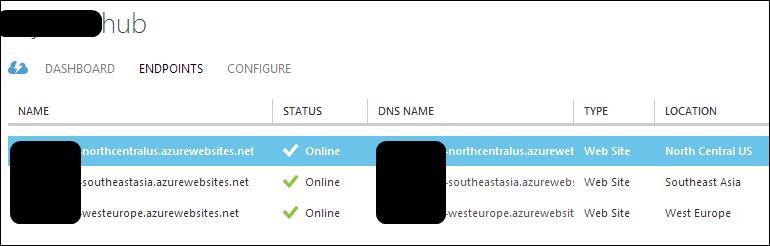
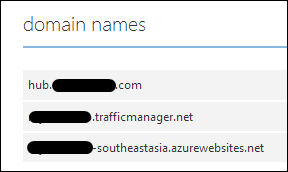
I change my DNS CNAME to point to the Traffic Manager, NOT the original website. Then I make sure the traffic manager knows about each of the Azure Website endpoints.
Then I make sure that my main CNAME is setup in my Azure Website, along with the Traffic Manager domain. Here's my DNSimple record:
And here's my Azure website configuration:
Important Note: You may be thinking, hang on, I though there was already load balancing built in to Azure Websites? It's important to remember that there's the load balancing that selects which data center, and there's the load balancing that selects an actual web server within a data center.
Also, you can choose between straight round-robin, failover (sites between datacenters), or Performance, when you have sites in geographic locations and you want the "closest" one to the user. That's what I chose. It's all automatic, which is nice.
Since the Traffic Manager is just going to resolve to a specific endpoint and all my endpoints already have a wildcard SSL, it all literally just works.
When I run NSLOOKUP myHub I get something like this:
>nslookup hub.mystartup.com
Server: ROUTER
Address: 10.71.1.1
Non-authoritative answer:
Name: ssl.mystartup-northcentralus.azurewebsites.net
Address: 23.96.211.345
Aliases: hub.mystartup.com
mystartup.trafficmanager.net
mystartup-northcentralus.azurewebsites.net
As I'm in Oregon, I get the closest data center. I asked friends via Skype in Australia, Germany, and Ireland to test and they each got one of the other data centers.
I can test for myself by using https://www.whatsmydns.net and seeing the different IPs from different locations.
This whole operation took about 45 minutes, and about 15 minutes of that was waiting for DNS to propagate.
In less than an hour went from a small prototype in a data center in Chicago and then scaled it out to datacenters globally and added SSL.
Magical power.
Related Links
- Azure Friday - http://friday.azure.com and also on iTunes!
- Setting up Traffic Manager
- Setting up Custom DNS Records to point to Azure Web Sites - with Stefan Schackow
- Moving a website to Azure while adding Continuous Deployment from Git
- Deploying TWO websites to Windows Azure from one Git Repository
Sponsor: Big thanks to Aspose for sponsoring the blog feed this week. Aspose.Total for .NET has all the APIs you need to create, manipulate and convert Microsoft Office documents and a host of other file formats in your applications. Curious? Start a free trial today.
About Scott
Scott Hanselman is a former professor, former Chief Architect in finance, now speaker, consultant, father, diabetic, and Microsoft employee. He is a failed stand-up comic, a cornrower, and a book author.
About Newsletter
You installed the SSL cert in central US to start, did you also install it in the other regions or were those different certs? At the end, Did you serve the certs from the load-balanced servers or did you reconfigure the load balancer to serve the SSL cert?
Great article.
//Morten
Thanks for sharing this Scott.
- Roland
I am hoping you or someone is able to point out a solution for the above issues or better still that I am wrong or confused because needing to access data is not an uncommon scenario :)
//Dennis
Great article btw.
Isuru
I have the same question as BB and Beyers Cronje.
If I have a SQL Azure on the same data center where the original site is, what would be the best approach to replicate to the other two? I don't think that having the server on Asia query the server on NorthCentral US is going to be that good for performance
My questions are:
When should I use one or the other?
Do I need to use them together, or is there a case where I should use websites with worker roles for example?
If I put all of the updates in the webjobs/worker roles, and I have one storage for each website, should I use the secondary storage connection string or should I replicate the data between the storages manually?
As for deploying to multiple sites - you could, instead of pushing straight from your local git repo, setup deployment from github/bitbucket(/dropbox?), so that you will only push once, and have webhooks take care of publishing the newest and sweetest code to all locations!
Azure WebSites *is* sweet.
Just curious what you're using on the backend? SQL Database? Or are you running your own SQL Server VMs? Or, are you using something NoSQL like Mongo?
Just curious what route you went for persistence.
My assumption is that I need employ some method data synchronizing on the back-end or try to use front-end caching solutions to keep as much data on the edge and possibly leave the profile/order data at one location and leave the fluff up front.
D.
1) Create a website and sql db for each region, then create a sync group for the sql dbs, then add a cdn that uses your storage account, then do the traffic manager stuff above.
2) As above but leave as single db and create VNETS between the regions.
In both cases could also use new redis cache on top.
In our situation it looks like there may be some room for reducing costs by choosing smaller website sizes and locally redundant sql db (in the case of using multiple dbs + sync group) now that traffic will be load balanced ?
Or pay for the tech support package. BUT a follow up post on the data side of things would obviously be well received.
Thanks,
Karl
Comments are closed.